
During pregnancy, a hormonal upheaval takes place in the body of the mother-to-be. You must have noticed that it is not without consequences! Do you know what exactly pregnancy hormones are used for?
In fact, they are messengers; their role is always the same: to transmit orders from their place of production to their target (an organ of the body). Once released into the blood, hormones search for the organ in question, then once found, they attach themselves to it and transmit the order they have received.
Contents
Fertilization: first encounter with pregnancy hormones
Following the release of the egg, the follicle becomes a corpus luteum. If there is intercourse, the egg will meet a sperm, and an embryo will be created. The embryo can then anchor itself in the uterine wall. It is the start of great hormonal upheaval, the first encounter with pregnancy hormones! For nine months, hormones are produced in very large quantities to support the development and nutrition of the fetus.
Let the hormonal upheaval begin!
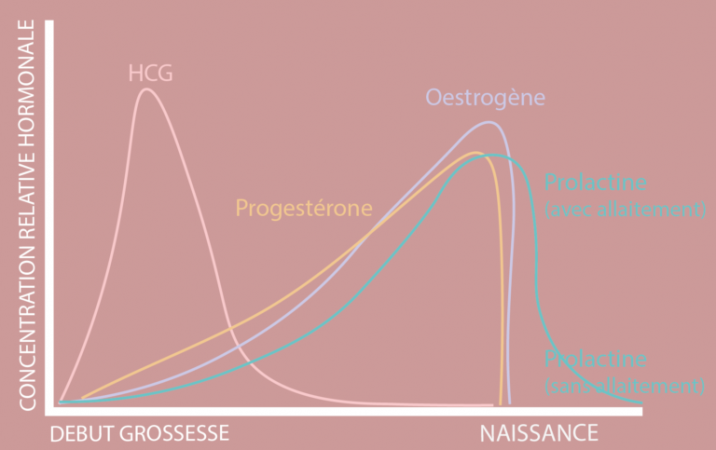
From the first days after fertilization, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) is secreted in large quantities. It will help maintain the yellow body. The latter will thus be able to continue to produce estrogen and progesterone, which will help maintain the embryo and stop menstruation for the next 9 months.
HCG is well known because it is the pregnancy hormone that will be measured during the pregnancy test if it is positive. It is the large quantity of HCG, which in general will cause nausea… Fortunately, from the third month, the level of HCG decreases with nausea (phew…)!
Progesterone
Progesterone is produced in large amounts throughout pregnancy. It will allow the implantation of the embryo and the thickening of the uterine wall. Along with estrogen, they will promote breast development and preparation for lactation. Progesterone also causes sagging smooth muscles. The gut and heart become sluggish, which can lead to constipation and fainting. But rest assured, there are not only downsides! It is thanks to the progesterone that these feelings of fullness and fulfillment come to you.
Estrogen
Estrogen sees its rate explode during pregnancy; it can be multiplied by 1000! This hormone increases the blood volume needed to feed the baby with nutrients and oxygen. The small downside is that estrogen can cause water retention. At the height of its secretion, helped by the sun, it can promote the famous “mask of pregnancy” and unsightly pimples … Fortunately, the moisturizing power of estrogen gives, in most cases, angel skin and voluminous and shiny hair and a brown (or blonde) line on the stomach!
What about during childbirth?
During childbirth, the level of progesterone drops sharply, as does its relaxing effects: contractions can begin. Other hormones intervene to help release the newborn: oxytocin causes contractions! The endorphin keeps the pain bearable, and finally, the peak of adrenaline in the final phase allows the delivery. After childbirth, hormone levels will gradually return to normal, with the exception of prolactin which helps to breastfeed in case the mom is breastfeeding the baby.
Now that you know the exact reason for all these upheavals, you can tell it is the fault of pregnancy hormones!