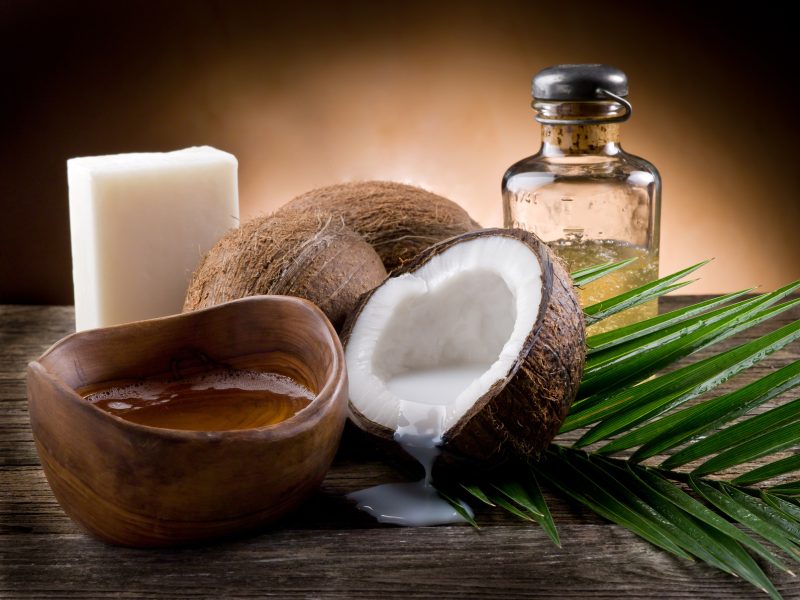

Coconut is one of the most versatile products that exist. It has contributions both from the nutritional point of view and aesthetics. But at the same time, science has begun to warn about the contraindications of coconut oil.
Faced with the properties and benefits of coconut oil, there is an acute controversy that has not yet been settled. The substance is composed of lauric, caprylic, and capric acid. This implies a high saturated fat content, so its regular intake can be harmful.
Contents
Coconut oil and its properties
For many, coconut oil falls into the category of famous superfoods thanks to its properties. It is used as a moisturizer for skin and hair. It is mixed with sugar, makes a good exfoliant, and can replace conditioner and hair removal foam. In some cases, it is also used as a make-up remover.
The point is that coconut oil is 100% fat. Between 80 and 90% is saturated fat. That is why it becomes compact at room temperature or in the cold.
Now, there is coconut oil made from 100% medium-chain triglycerides. These are absorbed very quickly by the body, promoting satiety and preventing fat storage.
However, the coconut oils sold in the market do not have the above formulation. They are not made with medium-chain triglycerides but with long-chain ones. In this case, the effect is the opposite: slower absorption and increased fat storage.
Coconut oil contraindications
There is no conclusive data on the benefits and harms caused by coconut oil. A study by Dr. Michael Mosley 2018 showed that this product increased bad cholesterol and good cholesterol.
Scientists agree that more research is required to reach a definitive conclusion. Meanwhile, doctors and nutritionists advise against using the product in the following cases.
People with high cholesterol
People with bad cholesterol or high LDL should be considered among the main contraindications for consuming coconut oil. As already indicated, the available evidence is ambiguous in this regard. Until more information is available, it is best to prevent possible damage.
Tendency to indigestion
This type of oil is not exactly the easiest to digest. If someone has food sensitivities, it is best not to consume this product, as it can irritate the intestinal mucosa.
Heart disease and hypertension
Saturated fats are deposited on the walls of the arteries. This causes blood flow to become blocked. Under these conditions, concomitant arterial hypertension may appear, increasing the risk of heart failure and heart attack.
Diabetes
People who have diabetes should stay away from coconut oil. Its continued use promotes a significant increase in blood glucose. Insulin sensitivity may also be affected.
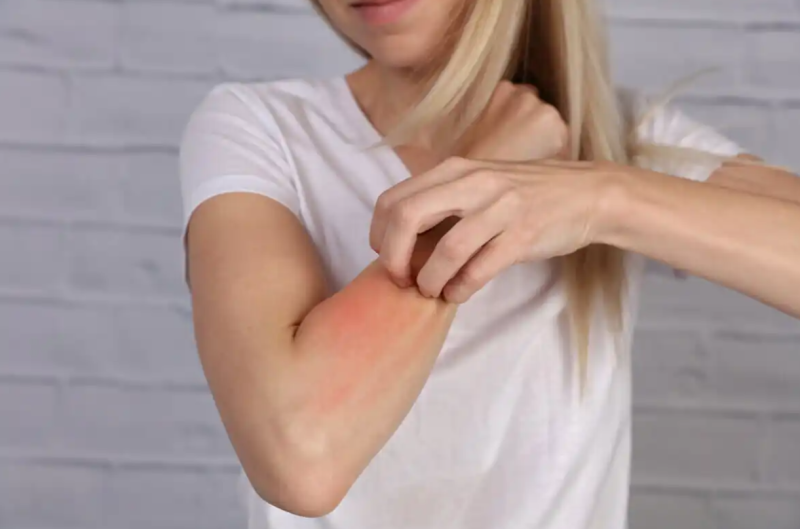
skin allergies
Coconut oil can cause an allergic skin reaction. The effects are inflammation, itching, and hives. If the response is more severe, vomiting and breathing problems may occur.
Prefer extra virgin coconut oil
In any case, opting for extra virgin coconut oil is indicated. In general terms, these types of fats should be avoided when they are refined and hydrogenated. Unfortunately, they are the ones most often found in the supermarket and at a cheap price.
Extra virgin coconut oil is made from the extraction of coconut milk. This is then left in its natural, unrefined state. Therefore, its appearance is not as white or shiny as the traditional commercial, but much healthier.