Astaxanthin is a carotenoid pigment of marine origin that has become popular in the market for its interesting medicinal properties. Specifically, it is found in trout, microalgae, and shrimp, among other marine species. However, it is distributed in the form of supplements to promote well-being.
According to a review published in Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, this substance has a powerful antioxidant effect that helps protect the body from the impact of oxidative stress. Added to this, antibacterial, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory properties are attributed. What are its uses?
Contents
Properties and uses of astaxanthin
Astaxanthin supplements stand out on the market due to studies that speak of its properties. The substance is a red pigment produced by unicellular algae Haematococcus pluvialis and fungi such as Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous when they find themselves in conditions where their environment is degraded and they are stressed by lack of nutrients.
It is also present in animals that feed on these algae, such as salmon, red trout, crustaceans, and bream. Likewise, it is manufactured synthetically, which has expanded its presence in the market.
As a study in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity explains, astaxanthin is a carotenoid valued for its antioxidant qualities. To be more precise, it has shown potential as an anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, immune system stimulant, antitumor, and cardiovascular ally. In the following space, we detail its main medicinal uses.
Skin health
The antioxidant potential of astaxanthin is used to care for the health of the skin. Some companies have begun to include it as a component of products to smooth wrinkles and reduce the signs of aging.
On this, a study disclosed through Acta Biochimica Polonica reported that the combination of topical and oral doses of the carotenoid showed positive effects against spots and wrinkles. It even seems helpful in retaining moisture in the skin.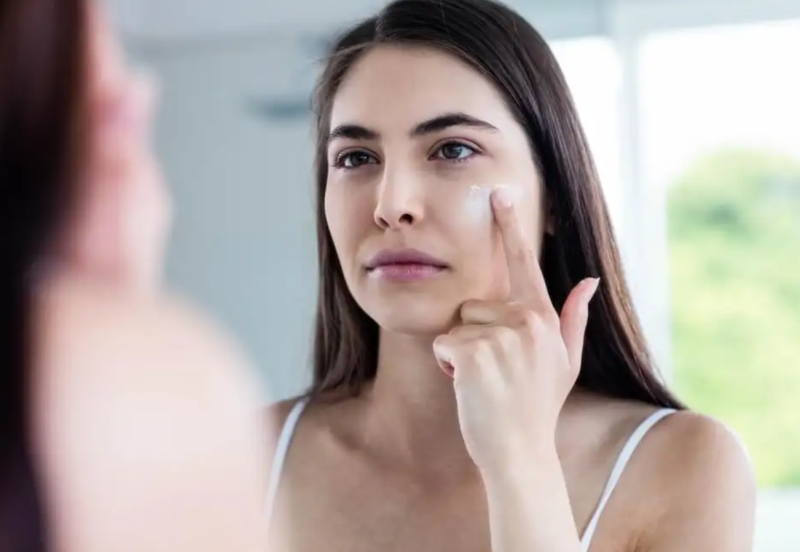
Heart health
Due to its ability to inhibit the adverse effects of free radicals, astaxanthin benefits heart health. In particular, it seems to improve circulation and the levels of elastin and thickness of the arterial walls.
Thus, as exposed by research in Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, it exerts an antihypertensive effect. By the way, it minimizes the risk of heart attacks and angina.
Joint pain
The evidence on the benefits of astaxanthin against joint pain is still limited. Still, it is believed to potentially develop future treatments for arthritis, osteoarthritis, and carpal tunnel syndrome. The reason? Its anti-inflammatory properties seem to contribute to the relief of symptoms.
Muscle health
Astaxanthin supplements can become allies for muscle recovery. Although clinical trials are lacking to determine its effects in humans, a study in mice determined that it helps prevent exercise-induced muscle and skeletal damage. It even seems to help improve physical resistance.
Brain
The medical journal Marine Drugs highlights astaxanthin supplements for their brain health properties. Specifically, it details that its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant qualities have preventive effects against neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Another study in GeroScience supports these properties and adds that the substance can potentially promote or maintain neuronal plasticity.
Antitumor
Remember that supplements are not a cancer treatment; this carotenoid is no exception. Even so, the substance has been the research focus on how it can affect cancer treatment.
Thus, a study shared in the International Journal of Molecular Medicine determined that it has short- and long-term benefits against breast cancer. Via the journal Antioxidants, other research supports these effects. The problem is that research is limited, given the high cost of purified astaxanthin.
Other possible benefits of astaxanthin
- Research in the journal Nutrients suggests that astaxanthin protects against ultraviolet (UV)-induced skin deterioration. It does not replace the use of sunscreen, but it is a complement to mitigate the impact of the sun.
- In an Asian Journal of Andrology publication, astaxanthin was reported to affect male fertility positively. To be more precise, improvements in sperm parameters were observed.
- This variety of supplements may help improve the immune response in humans, according to research shared in Nutrition & Metabolism.
- Digestive health also seems to benefit from the effects of this substance. Not only because of its antibacterial properties that help prevent intestinal infections but also because it improves the microbiota composition.

Recommended doses and contraindications of astaxanthin
For now, an exact dose for astaxanthin consumption has not been established. In general, manufacturers suggest 2 to 10 milligrams. Although the substance can be obtained naturally with some foods, it isn’t easy to reach that recommended amount. Therefore, it is necessary to resort to supplementation.
For most healthy adults, it is considered safe and tolerable. In any case, it is contraindicated in the following circumstances:
- People with low calcium levels.
- Patients are allergic or sensitive to this substance.
- People with low blood pressure.
- Thyroid disorders.
- Hormonal problems.
- Osteoporosis.
It is necessary to consult a doctor if you have underlying diseases or are taking medication. Do not rule out possible interactions.
Astaxanthin: A Popular Antioxidant Supplement
That astaxanthin has gained popularity as a dietary supplement is no coincidence. A wide variety of studies support the beneficial effects of its concentration of antioxidants. Therefore, it can be a good option for those who seek to increase their well-being.
In any case, it is advisable to consult a doctor before taking it regularly. The professional will determine what dose to ingest and if its simultaneous consumption with medicines is safe.