Taking care of our skin is essential for many reasons. In principle, this is the protective layer of our body, so taking care of it is necessary to protect the rest of our body. In addition, any damage it suffers will be visible, compromising our comfort and personal image.
Fungi are microorganisms that can inhabit the skin surface without causing any problems. However, several situations favor their proliferation and lead to skin infection, known as cutaneous mycosis. Such is the case of humidity, heat, and poor hygiene.
In this sense, it is vital to take care of our skin and identify if we suffer from an infection that needs medical attention. This way, we can cure it quickly and avoid marks or sequelae.
Contents
Are all skin fungi the same?
Just as there are no single animal or plant species, the kingdom of fungi also comprises various organisms. Some of them usually affect humans and cause skin infections. Five fungal infections can cause spots, itching, and even pain.
1. Ringworm
Dermatophytosis, commonly known as “ringworm,” is an infection caused by fungi called dermatophytes. According to studies, the most frequent are the genus Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton agents. In humans, the incubation period is 1 to 2 weeks before symptoms of infection manifest.
Dermatophytes grow best in a warm and humid environment, being more common in tropical and subtropical regions. They also multiply in closed or poorly ventilated spaces and clothing that suffers from excessive sweating and sports objects or machines.
In general, they increase only in tissues that accumulate keratin or “dead tissue,” such as hair, nails, and the outer layer of the skin. They also stop their spread when they come into contact with living cells or areas of inflammation.
They are transmitted by contact with another host. The infection usually starts in the growing hair or the outermost part of the skin, known as the ‘stratum corneum,’ and spreads from there.
Ringworms are classified according to the area of the body they affect. For example, tinea capitis affects the hair and scalp. The physical attacks the skin of the trunk, extremities, and face. And likewise, ringworm of the hand is another common infection that affects the palms and makes them scaly.
A very common ringworm is that of the foot, better known as ” athlete’s foot.” Humid and warm environments: gyms’ utensils, sportswear, and changing rooms are ideal for these fungi to invade the skin. However, anyone is prone to this infection.
How to identify this type of fungus?
You can know if you have ringworm problems if you present the following:
- Itching or burning
- Redness of the skin in the form of rings.
- Blisters.
- Desquamation of the skin.
- Clear center lesions.
2. Candid
According to a publication in the Revista Médica Clínica Los Condes, candidiasis is an infection caused by yeasts of the genus Candida, the most common being Candida albicans. In general, these microorganisms are part of the normal microbiota of the skin and some mucous membranes, such as the mouth or vagina.
The infection occurs, among other causes, when our antibodies cannot defend ourselves adequately. This can happen when we have a depressed immune system or take antibiotics without professional supervision. It is also known that this infection can occur from wearing tight clothing or medical treatments, such as broad-spectrum antibiotics. Although this mycosis can affect any body part, it is common in areas of the skin with folds, such as the armpits, the lower part of the breasts, the intergluteal area, and the groin.
In addition, these yeasts can infect the mucous membranes and even the esophagus and lungs. As several studies point out, Candida is the central germ involved in diaper rash in babies due to the humidity that remains in the area.How to identify this type of fungus?
- Red lesions with surrounding pimples or cysts.
- Peripheral desquamation.
- Central fissure, in case of affecting the skin folds.
- I was itching and burning.
- Pain and discomfort.
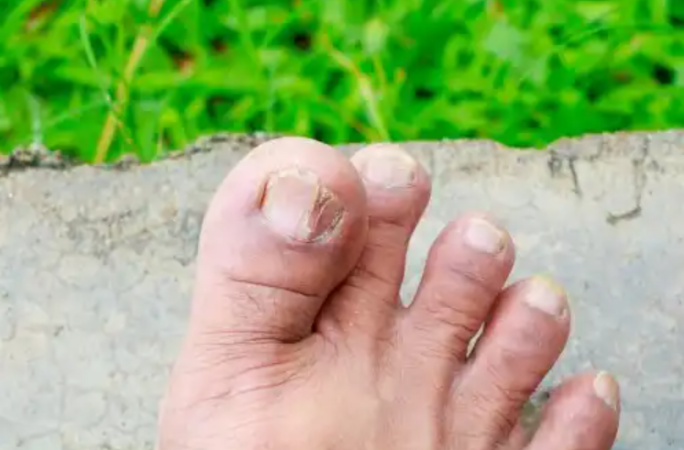
3. Onychomycosis
Fungal infections can also affect the nails, receiving the name onychomycosis. Many of the etiological agents are dermatophytes, so they can be included within ringworm under the name tinea ungueal, which describes the nail’s structure. However, it can also be caused by other fungi that affect the skin, such as molds and yeasts.
Multiple studies show that onychomycosis is the most common nail infection, accounting for up to 30% of all cases. Anyone can get this infection. However, people with diabetes and immunocompromised people are at higher risk. In the case of the former, there is a general prevalence of onychomycosis of 32.5%. As various scientific literature points out, this nail infection in this age group can be complicated by developing ulcers, gangrene, and osteomyelitis.
Fungus most often affects the toenails. In general, the nail unit itself can be infected, as well as the surrounding skin, and even spread to other nails. Treatment of this fungal infection requires medical supervision and often involves a combination of topical and oral therapy.
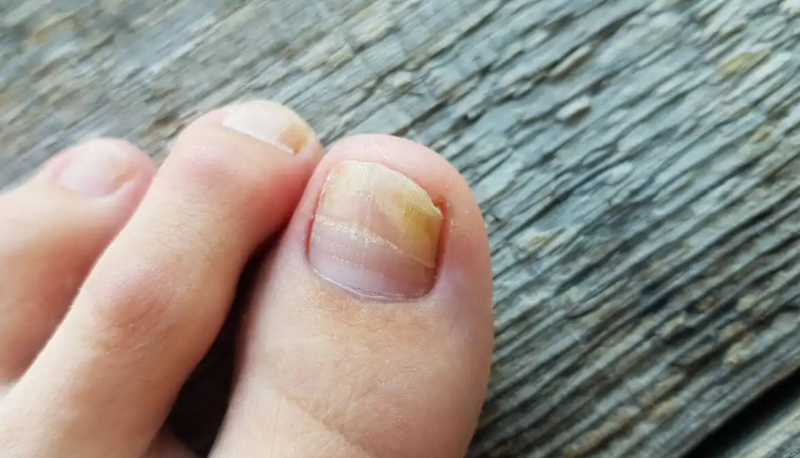
How to identify this type of fungus?
- Color changes in the nails, turning whiter or yellowish.
- Alteration in the shape of the nail plate.
- They are weakening and fissures in the nail.
- Thickening.
- Pain in severe cases.
4. Tinea versicolor
Pityriasis Versicolor is a type of fungal skin infection caused by yeast. The most common etiologic agent is Malassezia furfur. It is usually found on the skin as part of the normal flora. However, it can become a pathogen under certain conditions.
The fungus can produce azelaic acid, which prevents melanin production, causing classic symptoms. This disease has a universal distribution. However, studies suggest it is more frequent in tropical and subtropical countries. Likewise, it is more common in young people and young adults.
The characteristic lesions of Pityriasis versicolor can appear anywhere on the body. One of the most frequent locations is the chest, but it is also possible to see it on the neck, face, and arms.
How to identify this type of fungus?
- Whitish, or yellowish, and rounded spots.
- Light peeling of the skin.
- I am itching or stinging in the lesions.
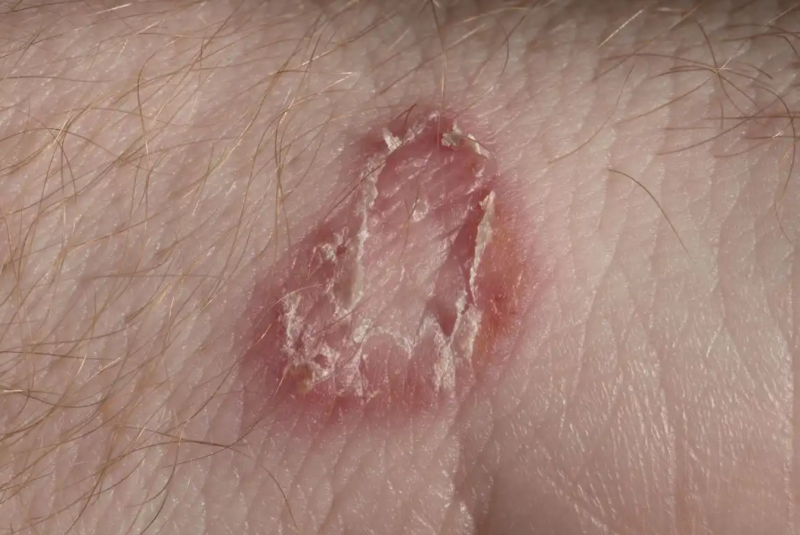
5. Sporotrichosis
According to an investigation by the Revista Iberoamericana de Micología, it is a very frequent mycosis in Latin America caused by a mold called Sporothrix schenckii. The etiological agent inhabits different types of moss, rose bushes, manure, and hay bales. Its distribution means that the most affected populations are gardeners and farmers.
The fungus penetrates the skin through minor wounds, usually due to punctures with plant thorns. Fortunately, it cannot be transmitted from person to person. In addition, hematogenous spread to other tissues is rare, so the lesions are usually confined to a specific area.
How to identify this type of fungus?
- Lump or papule, single or multiple, of variable size.
- A painless lesion that progressively increases in size.
- In the case of lymphatic involvement, the lesions are arranged linearly.
Over the days, the lesions will become necrotic and resemble a boil. In addition, they evolve and become ulcers that take time to heal.
How are cutaneous mycoses treated?
The treatment plan for fungal skin infections varies depending on the microorganism involved and the severity of the clinical picture. In most cases, topical antifungal drug therapy is effective as emulsions, creams, ointments, or solutions. Some of the most used are the following:
- Ketoconazole.
- Itraconazole and fluconazole.
- naphthyline.
- Terbinafine.
Similarly, systemic antifungals can be used orally or parenterally for extensive lesions or not responding to topical treatment. In certain mycoses, corticosteroids can help relieve itching under strict medical prescriptions.
Prevention of skin fungus is essential.
Good hygiene is crucial to prevent the proliferation of fungus on the skin. Similarly, it is advisable not to wear tight clothing and closed shoes during hot times since humidity favors these infections.
In addition, personal items or underwear should not be shared. In case of identifying a possible superficial mycosis, visit your trusted dermatologist.