Iron is an essential element in the human body for the formation of hemoglobin and oxygen transport. It moves through the bloodstream by various proteins, including transferrin. Are you interested in knowing what this molecule is like and its normal levels?
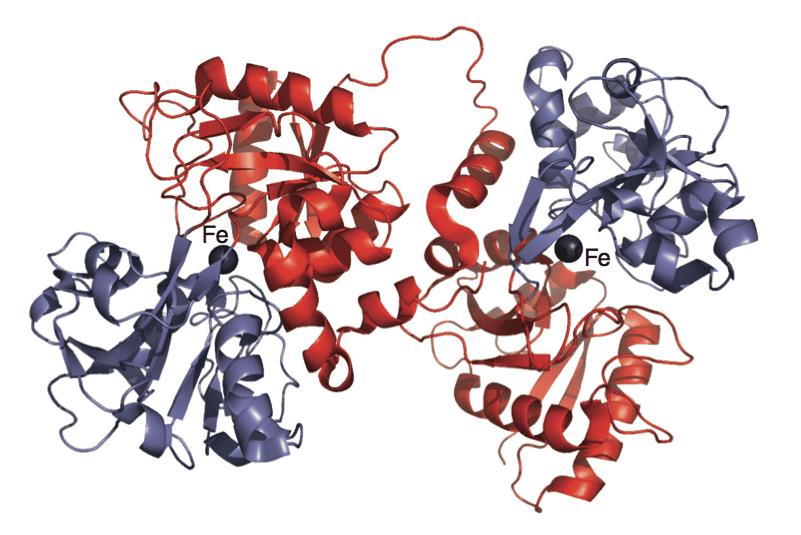
Transferrin is actively involved in iron metabolism. It is a protein whose function is to fix and transport iron in the blood, which is why it is also called iron-binding protein. In addition, it can transport other metals in the body, such as manganese, copper, gallium, and titanium.
Transferrin levels can be determined through blood tests in laboratories. Its concentration may vary depending on the age, sex, and general condition of the patient. It is beneficial to identify alterations in red blood cells.
Contents
What is transferrin used for in the human body?
Transferrin is a glycoprotein produced mainly in the liver. According to studies, it has an average half-life in the blood of 8 to 10 days. Its function is to take the iron absorbed in the intestine and the iron obtained from the destruction of old red blood cells to transport it in the blood.
Iron can be found in ferric (Fe 3+ ) and ferrous (Fe 2+ ). Each transferrin molecule can capture two iron ions in the ferric state.
In this way, the protein that does not have iron is called apo transferrin, mono ferric transferrin when it has a single iron atom, and ferric when it has 2.
Under normal conditions, only one-third of the available transferrin is used for iron transport. If the body uses all available transferrin, it is called saturated transferrin. Faced with this situation, iron will not be able to be captured anymore and will accumulate in the liver.
Research suggests that of all the iron carried by transferrin, 70-90% is taken up by the bone marrow to produce hemoglobin. The rest will be used to manufacture enzymes and coordinate various metabolic reactions.
How are blood transferrin levels measured?
The determination of transferrin levels can be performed directly or indirectly. In this sense, the direct method identifies the exact concentration of this molecule from a blood sample. The indirect method is also called total iron binding capacity (TBC).
The CTFH measures the amount of iron-binding proteins, including transferrin. This test is usually cheaper and more straightforward, so some specialists use it more. Both methods are used to calculate the amount of circulating iron, so we will see an elevation of transferrin and CTFH when faced with a mineral deficiency.
This assessment must be made with the patient fasting for 8 to 12 hours. Additionally, levels and complete hematology, blood chemistry, iron level, and ferritin concentration are often ordered.Normal values
- Men: 215 to 360 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl).
- Women: 250 to 370 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl).
- Children: 200 to 350 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl).
On the other hand, normal CTFH levels range between 250 and 350 micrograms per deciliter (µg/dl). The result changes depending on the sex, age, and state of health of the person. In addition, each laboratory offers its own normality and standardization criteria.
High transferrin
In most cases, the transferrin concentration differentiates between microcytic anemias. The red blood cells are smaller than usual in this type of anemia.
Transferrin is elevated when values above 360 mg/dl are obtained in men and 370 mg/dl in women. Studies affirm that the most common cause of high transferrin is iron deficiency anemia or iron deficiency. Other causes include the following:
- Pregnancy.
- Polycythemia.
- Oral contraceptives.
- Estrogen hormone therapy.
low transferrin
There is talk of low transferrin or hypotransferrinemia when this protein in the blood is below 215 mg/dl in men and 250 mg/dl in women. Among the causes of this phenomenon are the following:
- Thalassemia.
- Malnutrition.
- sickle cell disease
- Kidney diseases.
- Sideroblastic anemia.
- Extensive burns.
- Repeated infections.
- Liver disorders, such as cirrhosis.
- Anemia is typical of chronic diseases, such as cancer.
- Use of medications, such as chloramphenicol and glucocorticoids.
What is the transferrin saturation index?
Transferrin is capable of binding two iron ions. However, most of these molecules are usually not fully occupied. In this sense, the transferrin saturation index evaluates the percentage of these proteins occupied by iron.
Under normal conditions, the value corresponds to 20-50% of the total transferrin. However, iron deficiency anemia increases since there is insufficient iron to transport by transferrin.
Is it possible to normalize the levels?
Transferrin levels in the blood are directly dependent on the iron concentration and the state of the red blood cells. In most cases, low levels are the product of mineral deficiency, so it is recommended to increase its consumption.
This can be achieved by increasing the intake of the following foods:
- Eggs.
- Red meat and liver.
- Lentils and chickpeas.
- Fish and shellfish.
- Spinach and peaches.
If transferrin levels are decreased, it is necessary to solve the underlying cause so that they return to normal. Health professionals must assess since they are the only ones trained to identify and treat these diseases.
An essential protein in iron metabolism
Transferrin is an essential molecule for the transport of iron in the body. Its deficiency is related to different types of anemia, such as thalassemia, sickle cell disease, and anemia of chronic diseases. On the other hand, the excess is associated with iron deficiency, pregnancy, and contraceptives.